It is of the utmost significance that patients in hospital beds be kept safe, especially those who are suffering from life-threatening illnesses. Electrically adjusted medical beds provide patients with the comfort, safety, and convenience they seek through the use of electric actuators and linear motion technology. This article will discuss and investigate the potential benefits of medical electric beds for reducing the number of injuries and deaths caused by patient falls in healthcare facilities. Medical electric beds are a modern alternative to traditional hospital beds, featuring a host of helpful features and technology that improve patients' comfort and safety while reducing healthcare workers' workload.
High Rates of Slips, Trips, and Falls Among Hospital Patients
There is always the looming danger of accidents happening, even in the carefully planned setting of a hospital. Even with the best efforts of medical staff, people in hospitals still have a troublingly high rate of falls. These occurrences not only endanger patients, but they also put a strain on hospitals' already limited resources and go against the entire principle of providing care in a safe and effective manner. In this light, the serious problem of the alarmingly increasing number of falls and injuries that occur in healthcare facilities becomes apparent, calling for a preventative and creative strategy to ensure the wellbeing of patients and the integrity of their therapeutic surroundings.
Importance of Patient Safety and Well-Being in Healthcare Facilities
The health and safety of patients are non-negotiable imperatives that must always be met in any healthcare setting if professionals are to act ethically. The maintenance of patient safety is of utmost importance within the complex network of diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation. Maintaining a safe environment for patients to receive medical care does more than just adhere to the "do no harm" principle; it also builds trust and confidence between patients and their healthcare professionals.
Safeguarding patients is a top priority in healthcare institutions since it affects all other areas of treatment. Care providers and patients are less likely to suffer negative outcomes when they are provided with a secure setting, as medical mistakes, adverse events, and avoidable consequences are less likely to occur. Meanwhile, the emotional and mental well-being of a patient is just as important as their physical health. Patients are vulnerable people who place their health and life in the hands of healthcare providers; this comprehensive approach to wellness recognises this.
In addition, a culture of continuous improvement and responsibility is cultivated in healthcare facilities when patient safety and well-being are prioritised. As a result, it promotes the use of well-tested procedures, the utilisation of best-practices based on scientific data, and the incorporation of technical advances in order to lessen adverse effects and maximise positive results. By prioritising patient safety, healthcare providers improve the quality of treatment they provide, which in turn benefits patients in terms of enhanced satisfaction with their care and improved health.
Putting patients' health and safety first in healthcare settings is not only the right thing to do from a moral standpoint, but also the foundation for effective public health policies and programmes. When people in need get the care they need in a secure and effective setting, it improves community health as a whole and puts less stress on healthcare providers.
Traditional vs. Medical Electric Beds
Patients' falls and injuries while in hospitals are major issues that need to be addressed. Electric beds with additional safeguards are frequently used in hospitals to combat this problem. The purpose of this study is to examine the relative efficacy of standard electric beds versus medical electric beds in reducing the risk of patient falls and subsequent injuries.
Conventional electric beds often only allow for a change in height and a few fixed positions. Patients and carers can benefit from their portability, but they may not have access to the latest fall-prevention technology. If there are side rails, they may not be adjustable or supportive enough for the individual patient, putting them at risk.
In order to lessen the likelihood of accidents from falls, modern medical electric beds are outfitted with a number of high-tech safety measures and individualised adjustments. These beds have motion detectors and other alarms to keep medical workers informed.
Ways to Prevent Falls and Injuries in Hospitals?
Fall Prevention Mechanisms
Adjustable side rails and bed exit alarms are only two of the many fall-prevention features included into modern medical electric beds. These devices take a proactive stance towards patient safety by limiting the possibility of falls and stopping patients from leaving their beds by accident.
Enhanced Patient Mobility
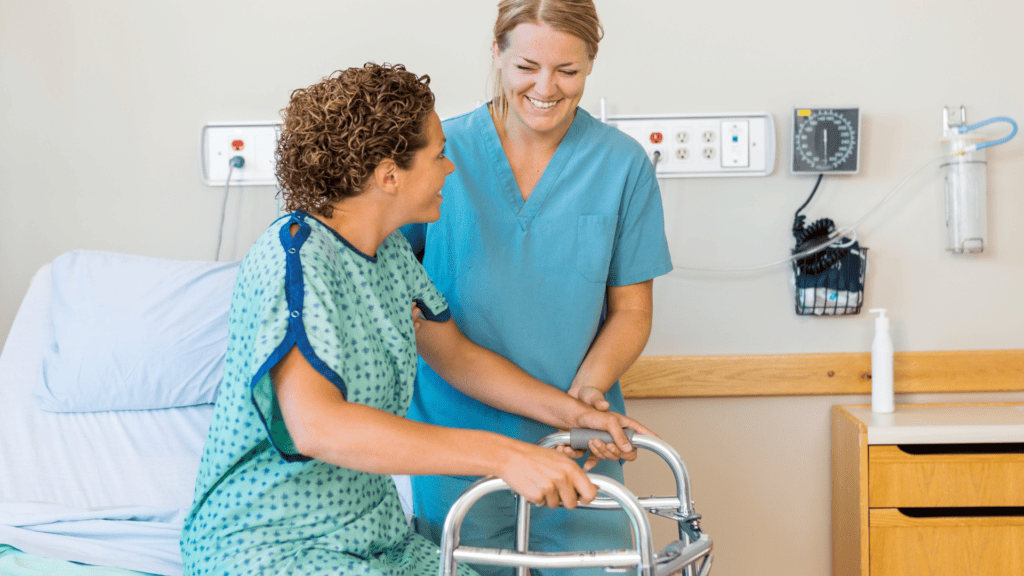
Medical electric beds are adjustable, so patients can change their positions without constant assistance from nurses or other carers. The patient's comfort and general well-being may grow as a result of this newfound freedom.
Real-time Monitoring and Alerts
Monitoring systems are commonly built into medical electric beds, allowing for early detection of any abnormalities in patient movement and the prompt notification of medical staff. Interventions and preventative measures can be implemented sooner thanks to this early warning.
Reduction of Caregiver Strain
Medical electric beds can greatly reduce the physical stress placed on medical staff by making patient transfers and repositioning much simpler. As a result, this can improve the health of carers and lessen the likelihood of harm occuring during the course of routine patient handling.
Patient-Centered Approach
Patient-centered care, which places an emphasis on comfort, safety, and autonomy, is reflected in the use of medical electric beds. As a result, patients may feel better about their healthcare experience overall.
This investigation is to answer the question of whether or not medical electric beds can effectively reduce the number of patient falls and injuries in healthcare facilities by conducting a systematic review of the relevant literature, case studies, and actual implementations. If healthcare professionals are able to weigh the benefits, drawbacks, and ramifications of adopting this novel approach, they will be better equipped to make decisions that will improve patient safety and well-being while also raising the bar for care quality as a whole.
Statistics and Prevalence of Falls Among Hospitalized Patients
One major and worrisome feature of patient safety in hospitals is the high incidence of patient falls. The statistical evidence for how common this problem is makes it all the more pressing that we take appropriate measures to deal with it and reduce the number of falls that occur:
- Incidence Rates: Studies show that between 2.3 to 7 falls occur per 1,000 patient days in acute care settings, demonstrating that hospital falls are prevalent. What this means in terms of actual numbers of falls each year is that they add up to significant numbers of patients being hurt and higher overall healthcare expenses.
- Elderly Patients: Statistics demonstrate that those aged 65 and up have a significantly increased chance of falling, making them a population at high risk of injury from falls in healthcare settings. Reduced mobility, poor balance, and age-related health concerns contribute to a disproportionate number of hospital admissions for this group as a result of injuries sustained in falls.
- Length of Stay Impact: Hospitalisation after a fall is often necessary for longer periods of time, which can strain already overburdened healthcare systems. Patients who encounter falls have a higher likelihood of requiring more medical attention, diagnostic testing, and interventions, all of which can extend their hospital stay.
- Consequences of Falls: Any number of injuries, from simple bumps and scrapes to more serious ones like broken bones, concussions, and internal bleeding, can arise from a fall. Both the patients' health and the hospital's ability to care for them are put at risk by these accidents.
- Financial Implications: Hospital falls have a huge monetary impact. Injuries sustained in a fall can result in a wide range of expenses, including medical care, hospitalisation, rehabilitation, and even legal action. The financial stakes make it all the more critical to implement measures to reduce the risk of falls.
- Underreporting: Factors including patient reluctance to reveal occurrences and different definitions of what constitutes a fall might lead to underreporting of falls, which is crucial to keep in mind. This indicates that the true prevalence of falls may be higher than estimated. When taken as a whole, these numbers highlight the urgent need for preventative measures to lower the rate of falls among hospitalised patients. The deployment of successful techniques, including the study of innovative solutions like medical electric beds, can play a crucial role in reducing the physical, emotional, and financial toll of falls in healthcare facilities, all of which are important for patient safety.
Identification of Common Causes and Risk Factors Contributing to Falls
Because of the severity of the injuries and consequences they can cause, falls pose a major threat to public health, especially among the elderly. In order to effectively avoid falls, it is necessary to first identify the most common causes and risk factors that contribute to them. Here are a few of the more important ones:
- Aging: Because of aging, a person's balance, muscle strength, and response time may deteriorate, making them more prone to falls.
- Weak Muscles: Weak muscles, especially in the lower body and core, can make it difficult to maintain stability and balance.
- Disorders of Gait and Balance: Uneven footing, poor balance, and shaky footing all contribute to an already high risk of falling.
- Issues with Vision: Impairments with vision, such as impaired depth perception, poor peripheral vision, and trouble responding to changes in lighting, can lead to erroneous perceptions of distance and the presence of obstacles.
- Medication Use: Some drugs, such as those that lower blood pressure, sedatives, and antidepressants, can produce dizziness, sleepiness, and a loss in cognitive function, raising the probability of falls.
- Environmental hazards: Environmental hazards such as excess furniture, hanging cords, rugs and tripping hazards such as wet flooring, uneven ground, poor lighting, and the absence of handrails or grab bars can all contribute to an unsafe environment.
- Diseases: Conditions like osteoporosis, arthritis, Parkinson's disease, stroke, and diabetes can impair movement and balance, increasing the likelihood of falls. Gait and balance can be compromised by foot issues such as painful feet, shoes that don't fit, and the use of inappropriate footwear.
- Cognitive Impairment: Memory problems, disorientation, and cognitive decline can lead to poor judgement and awareness of one's surroundings, which in turn increases the risk of falls.
- Poor nutrition: Poor nutrition and dehydration can increase the risk of falling by making people feel weak and dizzy.
- Influence of Alchohol: Drinking too much alcohol or using drugs can impair your motor skills and judgement, which can increase your risk of tripping and falling.
- Lifestyle: Sedentary lifestyles can cause muscle weakness, decreased bone density, and lower overall fitness, all of which contribute to falls. People who are afraid of falling are more likely to engage in inactive behaviours, have muscle weakness, and eventually experience a fall because of these changes in their normal movement patterns.
- Inadequate Use of Assistive Devices: Forgetting to use a cane, walker, or wheelchair when it's needed can significantly reduce stability and increase the likelihood of a fall.
- Underestimating Personal Sensitivity or Ignoring Risks: Many people may either be unaware of the potential risks in their environment or may underestimate their own sensitivity to falls.
A diversified strategy is necessary to reduce the prevalence of falls and mitigate the effects of these risk factors. Fall prevention measures include encouraging regular exercise to enhance strength and balance, evaluating and modifying medication regimens, eliminating environmental risks, encouraging good vision and foot care, and educating the public about these measures. Healthcare providers, carers, and individuals themselves all play important parts in reducing the risk of falls and maximising personal security.
Conclusion
Electric actuators and linear motion technologies have made possible the development of medical electric beds as a more comfortable, secure, and convenient alternative to conventional hospital beds. The purpose of these beds is to protect patients from harm by lowering the incidence of falls and accidents in hospitals.
The prevalence of slips, trips, and falls in healthcare facilities places unnecessary stress on staff and reduces the effectiveness of care provided. Healthcare institutions that put patients' well-being first foster an atmosphere of accountability and growth, which in turn leads to higher-quality care and greater patient satisfaction.
The incidence of falls in healthcare facilities is high, ranging from 2.3 to 7 per 1,000 patient days in hospitals alone. Many individuals are wounded and medical costs rise as a result of these accidents. Reduced mobility, poor balance, and age-related health concerns contribute to a disproportionate number of hospital admissions for patients aged 65 and up due to injuries sustained from falls. A patient's need for medical care, diagnostic testing, and intervention increases significantly after a fall and hospitalisation.
Medical treatment, hospitalisation, rehabilitation, and legal action all add up to hefty costs when someone suffers a fall. Patient reluctance to disclose incidents and differing definitions of what constitutes a fall can lead to underreporting, making it essential to address underreporting of falls. Knowing the most prevalent reasons for and risk factors associated with falls can help you prevent them. Ageing, muscle weakness, gait and balance abnormalities, visual problems, pharmaceutical side effects, environmental dangers, diseases, cognitive impairment, poor diet, alcohol impact, lifestyle, insufficient use of assistive equipment, and underestimating personal sensitivity or ignoring risks also contribute to this.
Content Summary
- It is of the utmost significance that patients in hospital beds be kept safe, especially those who are suffering from life-threatening illnesses.
- Electrically adjusted medical beds provide patients with the comfort, safety, and convenience they seek through the use of electric actuators and linear motion technology.
- Medical electric beds are a modern alternative to traditional hospital beds, featuring a host of helpful features and technology that improve patients' comfort and safety while reducing healthcare workers' workload.
- There is always the looming danger of accidents happening, even in the carefully planned setting of a hospital.
- Even with the best efforts of medical staff, people in hospitals still have a troublingly high rate of falls.
- These occurrences not only endanger patients, but they also put a strain on hospitals' already limited resources and go against the entire principle of providing care in a safe and effective manner.
- In this light, the serious problem of the alarmingly increasing number of falls and injuries that occur in healthcare facilities becomes apparent, calling for a preventative and creative strategy to ensure the wellbeing of patients and the integrity of their therapeutic surroundings.
- The health and safety of patients are non-negotiable imperatives that must always be met in any healthcare setting if professionals are to act ethically.
- The maintenance of patient safety is of utmost importance within the complex network of diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation.
- Maintaining a safe environment for patients to receive medical care does more than just adhere to the "do no harm" principle; it also builds trust and confidence between patients and their healthcare professionals.
- By prioritising patient safety, healthcare providers improve the quality of treatment they provide, which in turn benefits patients in terms of enhanced satisfaction with their care and improved health.
- Patients' falls and injuries while in hospitals are major issues that need to be addressed.
- Adjustable side rails and bed exit alarms are only two of the many fall-prevention features included into modern medical electric beds.
- These devices take a proactive stance towards patient safety by limiting the possibility of falls and stopping patients from leaving their beds by accident.
- Monitoring systems are commonly built into medical electric beds, allowing for early detection of any abnormalities in patient movement and the prompt notification of medical staff.
- This investigation is to answer the question of whether or not medical electric beds can effectively reduce the number of patient falls and injuries in healthcare facilities by conducting a systematic review of the relevant literature, case studies, and actual implementations.
- If healthcare professionals are able to weigh the benefits, drawbacks, and ramifications of adopting this novel approach, they will be better equipped to make decisions that will improve patient safety and well-being while also raising the bar for care quality as a whole.
- One major and worrisome feature of patient safety in hospitals is the high incidence of patient falls.
- Statistics demonstrate that those aged 65 and up have a significantly increased chance of falling, making them a population at high risk of injury from falls in healthcare settings.
- Reduced mobility, poor balance, and age-related health concerns contribute to a disproportionate number of hospital admissions for this group as a result of injuries sustained in falls.
- Injuries sustained in a fall can result in a wide range of expenses, including medical care, hospitalisation, rehabilitation, and even legal action.
- The financial stakes make it all the more critical to implement measures to reduce the risk of falls.
- When taken as a whole, these numbers highlight the urgent need for preventative measures to lower the rate of falls among hospitalised patients.
- The deployment of successful techniques, including the study of innovative solutions like medical electric beds, can play a crucial role in reducing the physical, emotional, and financial toll of falls in healthcare facilities, all of which are important for patient safety.
- Because of the severity of the injuries and consequences they can cause, falls pose a major threat to public health, especially among the elderly.
- In order to effectively avoid falls, it is necessary to first identify the most common causes and risk factors that contribute to them.
- Weak muscles, especially in the lower body and core, can make it difficult to maintain stability and balance.
- Uneven footing, poor balance, and shaky footing all contribute to an already high risk of falling.
- Impairments with vision, such as impaired depth perception, poor peripheral vision, and trouble responding to changes in lighting, can lead to erroneous perceptions of distance and the presence of obstacles.
- Some drugs, such as those that lower blood pressure, sedatives, and antidepressants, can produce dizziness, sleepiness, and a loss in cognitive function, raising the probability of falls.
- Environmental hazards such as excess furniture, hanging cords, rugs and tripping hazards such as wet flooring, uneven ground, poor lighting, and the absence of handrails or grab bars can all contribute to an unsafe environment.
- Conditions like osteoporosis, arthritis, Parkinson's disease, stroke, and diabetes can impair movement and balance, increasing the likelihood of falls.
- Gait and balance can be compromised by foot issues such as painful feet, shoes that don't fit, and the use of inappropriate footwear.
- Memory problems, disorientation, and cognitive decline can lead to poor judgement and awareness of one's surroundings, which in turn increases the risk of falls.
- Poor nutrition and dehydration can increase the risk of falling by making people feel weak and dizzy.
- Drinking too much alcohol or using drugs can impair your motor skills and judgement, which can increase your risk of tripping and falling.
- Sedentary lifestyles can cause muscle weakness, decreased bone density, and lower overall fitness, all of which contribute to falls.
- People who are afraid of falling are more likely to engage in inactive behaviours, have muscle weakness, and eventually experience a fall because of these changes in their normal movement patterns.
- Forgetting to use a cane, walker, or wheelchair when it's needed can significantly reduce stability and increase the likelihood of a fall.
- Many people may either be unaware of the potential risks in their environment or may underestimate their own sensitivity to falls.
- A diversified strategy is necessary to reduce the prevalence of falls and mitigate the effects of these risk factors.
- Fall prevention measures include encouraging regular exercise to enhance strength and balance, evaluating and modifying medication regimens, eliminating environmental risks, encouraging good vision and foot care, and educating the public about these measures.
- Healthcare providers, carers, and individuals themselves all play important parts in reducing the risk of falls and maximising personal security.
FAQs About Medical Bed
Medical beds support and place patients in hospitals. Medical beds contain head and foot elevation, allowing patients to select comfortable positions for their medical needs. These beds have extra accessories and safety measures, making them suited for hospitals, long-term care centres, and homecare.
Medical beds offer various benefits, including improved sleep quality, enhanced circulation, pain relief, and support for medical conditions. They are particularly helpful in post-surgery recovery and aiding patients with limited mobility.
Yes, there are homecare medical beds designed for home use. These beds offer similar features to hospital beds but are more compact and aesthetically suitable for home environments.
Adjustable medical beds have electric motors that power the adjustable components. Users or caregivers can control the bed's position using a remote or buttons on the side rails.
The coverage of medical beds varies depending on the patient's medical condition and insurance policy. Some medical beds may be partially or fully covered if deemed medically necessary. It's essential to check with the insurance provider for specific coverage details.