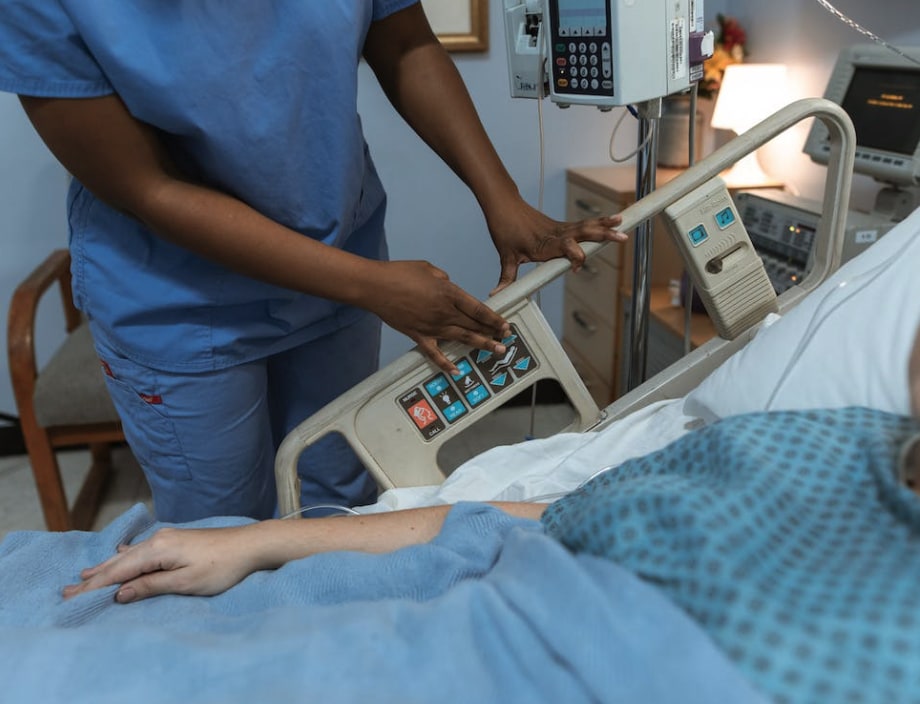
Hospital beds represent care, comfort, and recovery in the complex healthcare system, where patient safety is of the utmost importance. These medical devices are developed with care so that patients receive the best possible assistance during their stay. However, even in this setting for recovery, there is a potential threat: unsafe hospital beds. While patient care is a top priority in hospitals, a malfunctioning bed can present a host of problems that undermine healthcare's core foundation. In this article, we discuss the serious issue of the dangers posed by a broken hospital bed. We'll look at how a wide range of faults, from mechanical to electrical, can put patients at risk, change how doctors work, and even damage a hospital's reputation. By illuminating these dangers, we hope to emphasise the critical nature of fixing bed flaws and creating a culture of awareness that guarantees patients receive consistent care.
Types of Defective Hospital Beds
Mechanical and electrical components on hospital beds improve patients' quality of life and provide for easier access to care. When these components break down, however, a once-safe bed becomes a serious risk. Here are the two most common faults in hospital beds that can threaten patient health and safety:
Mechanical Defects
Hospital beds can have mechanical flaws if there is something wrong with its structure or the functioning of their moving parts. The bed's stability, patient support, and use may all suffer as a result of these flaws. A few typical cases are:
- Malfunctioning Adjustment Controls: Hospital beds typically have controls for adjusting the height, head, and feet. When these mechanisms malfunction or become unreliable, patients may be placed in precarious positions.
- Unstable Bed Frames: Wobbling or tilting caused by a faulty bed frame increases the danger of patients falling when getting in or out of bed.
- Faulty Side Railings: In order to avoid patient falls and provide necessary support, side rails are essential. Patient entrapment or falls might occur if the railings did not lock firmly in place.
Electrical Defects
Hospital beds' electrical components make them flexible and user-friendly. However, issues with these parts might pose dangers that lessen the quality of care provided to patients. Some common forms of electrical faults are:
- Non-responsive or Erratic Bed Height Adjustment: Beds with electronic height adjustment devices have the potential to malfunction, making patient transfers more difficult and even uncomfortable.
- Malfunctioning Bed Exit Alarms: When a patient tries to get out of bed, the alarm goes off and the staff is notified immediately. Patients could leave their beds unattended and suffer injuries if these alarms failed to alert carers.
- Issues with Electronic Controls for Head and Foot Adjustments: Patient comfort and medical efficiency can both benefit from beds with separate head and foot portions. When these mechanisms are flawed, patients may be placed in awkward situations that impede their healing.
If these mechanical and electrical problems aren't fixed, patients could suffer from everything from physical harm to treatment setbacks. If they care about their patients' health and safety, hospitals and other healthcare facilities cannot let up in their efforts to find and fix these problems.
Potential Risks of Defective Hospital Beds
Patients and medical staff alike are at risk from hospital beds that are malfunctioning owing to mechanical or electrical problems. Beyond direct physical harm, these dangers can affect how hospitals treat their patients, how well they prevent the spread of illness, and their standing in the community as a whole. Here is a rundown of some of the dangers that could arise from using a flawed hospital bed:
Patient Safety Risks
- Increased Fall Risks: Unstable bed frames, malfunctioning side railings, and erratic height adjustments can lead to patient falls when entering, exiting, or repositioning on the bed.
- Entrapment Hazards: Defective components might create gaps or spaces where patients can become trapped, leading to injury or distress.
Pressure Ulcers and Skin Issues
- Inadequate Pressure Redistribution: Beds with malfunctioning pressure redistribution features can lead to prolonged pressure on specific body areas, increasing the risk of pressure ulcers (bedsores).
- Impaired Repositioning: Beds with faulty adjustments can hinder proper patient repositioning, which is crucial for preventing pressure ulcers and promoting patient comfort.
Infection Control Compromises
- Difficulties in Cleaning: Defective bed components may be harder to clean and sanitize effectively, increasing the risk of transmitting infections between patients.
- Increased Direct Contact: Malfunctioning controls might necessitate more frequent direct contact by healthcare staff, potentially facilitating the spread of infections.
Staff Safety Concerns
- Patient Transfer Challenges: Unreliable bed adjustments can make it difficult for healthcare providers to transfer patients safely, increasing the risk of strain injuries for both patients and staff.
- Strain Injuries: Healthcare workers may experience strain injuries when attempting to maneuver patients due to bed-related difficulties.
Negative Impact on Patient Care
- Limitations in Medical Procedures: Beds with malfunctioning adjustments can hinder medical procedures that require specific patient positions, potentially affecting treatment outcomes.
- Patient Discomfort: Malfunctioning beds can cause discomfort, pain, and distress to patients, impeding their overall recovery process.
The urgency with which problems with hospital beds must be addressed and fixed is highlighted by these possible dangers. A hospital's commitment to providing high-quality medical care necessitates that it take preventative measures to guarantee that its beds are in good functioning order at all times. By reducing these dangers, medical centres can help patients feel safe and secure while they get better.
Consequences of Defective Hospital Beds
Having broken hospital beds in a healthcare facility is a major problem that has far-reaching consequences. Patients' well-being, the hospital's finances, and the doctors' and nurses' credibility could all suffer as a result. Let's take a closer look at the potential implications of having broken hospital beds:
Patient Health Complications
- Aggravation of Medical Conditions: Defective beds can exacerbate existing medical conditions or injuries, delaying patients' recovery and potentially leading to additional health complications.
- Pressure Ulcers and Infections: Inadequate pressure redistribution and infection control due to bed defects can result in the development of pressure ulcers and an increased risk of infections.
Increased Healthcare Costs
- Additional Medical Treatments: Complications arising from defective beds may necessitate additional medical treatments, interventions, and extended hospital stays, thereby increasing healthcare costs.
- Legal Liabilities: In severe cases, patients or their families might pursue legal action against the healthcare institution, leading to potential financial settlements, legal fees, and reputation damage.
Reputation Damage
- Negative Public Perception: Reports of defective beds and associated patient harm can tarnish the reputation of the hospital, eroding patient trust and discouraging potential patients from seeking care.
- Reduced Referrals: Healthcare facilities with a history of bed-related incidents might experience reduced referrals from medical professionals, impacting the overall patient volume.
Operational Disruptions
- Workflow Disruptions: Addressing bed defects can divert valuable staff time and resources away from patient care, affecting the efficiency of healthcare operations.
- Patient Flow: Delays caused by defective beds can disrupt patient flow and scheduling, leading to inefficient resource utilization and potential dissatisfaction among patients.
Employee Morale and Burnout
- Staff Frustration: Healthcare workers may become frustrated by the challenges posed by defective beds, potentially leading to reduced morale and job satisfaction.
- Increased Workload: Dealing with bed-related issues can add to the workload of healthcare providers, contributing to burnout and affecting the quality of care provided.
Regulatory and Accreditation Implications
- Regulatory Non-Compliance: Defective beds might lead to violations of healthcare regulations and standards, resulting in potential fines and loss of accreditation.
- Quality of Care Assessment: Accreditors and regulators may consider incidents related to bed defects when assessing the overall quality of care provided by the institution.
Patients aren't the only ones who suffer when hospitals use subpar equipment like broken beds. In order to avoid these outcomes, healthcare facilities must make regular maintenance, timely repairs, and vigilance top priorities. Patient safety, financial security, and a stellar reputation for excellence in care delivery are all bolstered by this practise.
Strategies to Prevent and Reduce Hospital Bed Failure
Properly functioning hospital equipment is crucial in the complex healthcare system, where patient well-being and safety are pillars. The hospital bed is the cornerstone of a patient's care, comfort, and rehabilitation from illness. But in this scene of healing, the spectre of faulty hospital beds hangs over patient safety and the credibility of medical care. Regular maintenance, continued staff training, keeping manufacturers accountable, and informing patients and their families about bed characteristics and potential risks are just some of the ways in which healthcare facilities can handle these concerns thoroughly. Doing so will allow healthcare facilities to set up a solid system that prevents and reduces the dangers linked with faulty hospital beds.
Proactive maintenance and routine inspections are the backbone of the strategy. Because of the complex nature of its mechanical and electrical systems, hospital beds require vigilant maintenance to function properly. The best way to prevent problems is to implement a strict maintenance schedule and have it carried out by trained professionals. This strategy includes routine checks of all mechanical and electrical parts of the bed. The goal of these checks is to catch minor indicators of wear, damage, or malfunction before they become major catastrophes.
Every second matters when it comes to taking care of patients. Issues must be dealt with quickly and efficiently. Repairing or replacing faulty parts quickly can stop problems from getting worse and creating safety hazards. Beds can continue to support patients safely and reliably as long as they are regularly maintained and any repairs are made promptly. This not only protects patients from danger but also creates an atmosphere where they can feel safe in the knowledge that their health is a top priority.
Staff members in a hospital setting are the first line of defence in ensuring patients are safe. Providing this hardworking staff with the education they need to spot, report, and fix bed issues is a top priority. Hospital beds have a number of controls and indicators of wear and tear that need to be covered in detail during training sessions. With this information at their disposal, healthcare workers can take an active role as sentinels, keeping an eye out for problems and alerting the appropriate teams as soon as they are noticed. When a patient's safety is at risk because of bed-related difficulties, staff members who have been trained in emergency protocols can respond quickly and effectively.
It is crucial to work together with bed makers and suppliers to stop faulty beds from reaching hospitals. Healthcare facilities can significantly lessen the likelihood of encountering faults by partnering with manufacturers who comply with industry safety standards and regulations. Choosing reliable vendors with solid guarantees and helpful service after the sale is essential to the success of this plan. This provides a safety net for healthcare facilities, allowing for the fast fixing of any flaws that may develop.
Additionally, it is critical to set up open lines of contact with the manufacturers. This facilitates a receptive atmosphere in which manufacturers can swiftly move to fix faults, as reported by healthcare facilities. This cooperation goes beyond the merely transactional in its focus on patient well-being, and it serves as further evidence of the dedication to patient safety.
Conclusion
In the intricate healthcare system, hospital beds play a crucial role in patient care, comfort, and recuperation. However, a patient's health and safety can be seriously jeopardised by a broken bed. Hospital beds can lose their steadiness, support, and utility if mechanical or electrical problems arise. Beds with broken adjustment knobs, frames that wobble, and handrails that don't stay in place are all examples of common mechanical failures. Bed exit alarms that don't work, electronic controls that are unreliable, and unresponsive beds are all examples of electrical problems that can negatively impact patient care.
Fall hazards, entry hazards, pressure ulcers, skin issues, insufficient pressure redistribution, impaired repositioning, infection control compromises, increased direct contact, staff safety concerns, transfer difficulties, strain injuries, procedure restrictions, and patient discomfort are all potential threats to patient safety. Hospital care, the prevention of disease transmission, and public trust are all threatened by these issues. These issues must be addressed and fixed if high-quality medical treatment is to be provided and if patients are to be comfortable while recovering.
Patients' health, the hospital's bottom line, and the medical staff's reputation can all take a hit if their beds aren't up to par. Patient health issues, such as pressure ulcers, infections, higher healthcare costs, legal liabilities, a negative public perception, fewer referrals, interrupted operations, slowed patient flow, demoralised staff, extra work, and failed quality-of-care assessments can all result from too many beds.
Patients' safety, the facility's financial stability, and its reputation for providing excellent treatment depend on regular inspections, prompt repairs, and constant vigilance. Healthcare facilities can establish a reliable strategy to minimise and lessen the risks connected with malfunctioning hospital beds by applying these measures.
Content Summary
- Hospital beds represent care, comfort, and recovery in the complex healthcare system, where patient safety is of the utmost importance.
- However, even in this setting for recovery, there is a potential threat: unsafe hospital beds.
- While patient care is a top priority in hospitals, a malfunctioning bed can present a host of problems that undermine healthcare's core foundation.
- We'll look at how a wide range of faults, from mechanical to electrical, can put patients at risk, change how doctors work, and even damage a hospital's reputation.
- By illuminating these dangers, we hope to emphasise the critical nature of fixing bed flawHs and creating a culture of awareness that guarantees patients receive consistent care.
- Mechanical and electrical components on hospital beds improve patients' quality of life and provide for easier access to care.
- When these components break down, however, a once-safe bed becomes a serious risk.
- Hospital beds can have mechanical flaws if there is something wrong with its structure or the functioning of their moving parts.
- When a patient tries to get out of bed, the alarm goes off and the staff is notified immediately.
- Patient comfort and medical efficiency can both benefit from beds with separate head and foot portions.
- If these mechanical and electrical problems aren't fixed, patients could suffer from everything from physical harm to treatment setbacks.
- If they care about their patients' health and safety, hospitals and other healthcare facilities cannot let up in their efforts to find and fix these problems.
- Patients and medical staff alike are at risk from hospital beds that are malfunctioning owing to mechanical or electrical problems.
- Beyond direct physical harm, these dangers can affect how hospitals treat their patients, how well they prevent the spread of illness, and their standing in the community as a whole.
- Unstable bed frames, malfunctioning side railings, and erratic height adjustments can lead to patient falls when entering, exiting, or repositioning on the bed.
- Beds with malfunctioning adjustments can hinder medical procedures that require specific patient positions, potentially affecting treatment outcomes.
- Malfunctioning beds can cause discomfort, pain, and distress to patients, impeding their overall recovery process.
- The urgency with which problems with hospital beds must be addressed and fixed is highlighted by these possible dangers.
- A hospital's commitment to providing high-quality medical care necessitates that it takes preventative measures to guarantee that its beds are in good functioning order at all times.
- Having broken hospital beds in a healthcare facility is a major problem that has far-reaching consequences.
- Patients' well-being, the hospital's finances, and the doctors' and nurses' credibility could all suffer as a result.
- Inadequate pressure redistribution and infection control due to bed defects can result in the development of pressure ulcers and an increased risk of infections.
- Complications arising from defective beds may necessitate additional medical treatments, interventions, and extended hospital stays, thereby increasing healthcare costs.
- Reports of defective beds and associated patient harm can tarnish the reputation of the hospital, eroding patient trust and discouraging potential patients from seeking care.
- Addressing bed defects can divert valuable staff time and resources away from patient care, affecting the efficiency of healthcare operations.
- Accreditors and regulators may consider incidents related to bed defects when assessing the overall quality of care provided by the institution.
- Patients aren't the only ones who suffer when hospitals use subpar equipment like broken beds.
- In order to avoid these outcomes, healthcare facilities must make regular maintenance, timely repairs, and vigilance top priorities.
- Patient safety, financial security, and a stellar reputation for excellence in care delivery are all bolstered by this practise.
- Properly functioning hospital equipment is crucial in the complex healthcare system, where patient well-being and safety are pillars.
- The hospital bed is the cornerstone of a patient's care, comfort, and rehabilitation from illness.
- But in this scene of healing, the spectre of faulty hospital beds hangs over patient safety and the credibility of medical care.
- Doing so will allow healthcare facilities to set up a solid system that prevents and reduces the dangers linked with faulty hospital beds.
- Proactive maintenance and routine inspections are the backbone of the strategy.
- Because of the complex nature of its mechanical and electrical systems, hospital beds require vigilant maintenance to function properly.
- The best way to prevent problems is to implement a strict maintenance schedule and have it carried out by trained professionals.
- This strategy includes routine checks of all mechanical and electrical parts of the bed.
- Every second matters when it comes to taking care of patients.
- Issues must be dealt with quickly and efficiently.
- Repairing or replacing faulty parts quickly can stop problems from getting worse and creating safety hazards.
- Beds can continue to support patients safely and reliably as long as they are regularly maintained and any repairs are made promptly.
- Staff members in a hospital setting are the first line of defence in ensuring patients are safe.
- Providing this hardworking staff with the education they need to spot, report, and fix bed issues is a top priority.
- Hospital beds have a number of controls and indicators of wear and tear that need to be covered in detail during training sessions.
- With this information at their disposal, healthcare workers can take an active role as sentinels, keeping an eye out for problems and alerting the appropriate teams as soon as they are noticed.
- When a patient's safety is at risk because of bed-related difficulties, staff members who have been trained in emergency protocols can respond quickly and effectively.
- It is crucial to work together with bed makers and suppliers to stop faulty beds from reaching hospitals.
- Healthcare facilities can significantly lessen the likelihood of encountering faults by partnering with manufacturers who comply with industry safety standards and regulations.
- Choosing reliable vendors with solid guarantees and helpful service after the sale is essential to the success of this plan.
- This provides a safety net for healthcare facilities, allowing for the fast fixing of any flaws that may develop.
- Additionally, it is critical to set up open lines of contact with the manufacturers.
- This facilitates a receptive atmosphere in which manufacturers can swiftly move to fix faults, as reported by healthcare facilities.
- This cooperation goes beyond the merely transactional in its focus on patient well-being, and it serves as further evidence of the dedication to patient safety.
FAQs About Medical Beds
Medical beds support and place patients in hospitals. Medical beds contain head and foot elevation, allowing patients to select comfortable positions for their medical needs. These beds have extra accessories and safety measures, making them suited for hospitals, long-term care centres, and homecare.
Medical beds offer various benefits, including improved sleep quality, enhanced circulation, pain relief, and support for medical conditions. They are particularly helpful in post-surgery recovery and aiding patients with limited mobility.
Yes, there are homecare medical beds designed for home use. These beds offer similar features to hospital beds but are more compact and aesthetically suitable for home environments.
Adjustable medical beds have electric motors that power the adjustable components. Users or caregivers can control the bed's position using a remote or buttons on the side rails.
The coverage of medical beds varies depending on the patient's medical condition and insurance policy. Some medical beds may be partially or fully covered if deemed medically necessary. It's essential to check with the insurance provider for specific coverage details.